Will Machine Learning Change Online Gambling Forever? 85% of Experts Say Yes
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are now used in over 90% of online and offline industries. But can ML truly revolutionize online gambling, too? More than 80% of the experts in the field think the answer is yes. This article explores several current and potential applications of AI in gaming, sports betting, security, responsible gambling initiatives and more. Discover how your gambling habits could change forever, thanks to AI.
- Is There a Future for AI in Online Casinos?
- How AI Became a Game-Changer for the Gaming Industry
- Taking Gambling to the Next Level with Artificial Intelligence
- Can AI help casinos cut down on problem gambling?
- Next-Gen Gambling Awakens: Harnessing the Power of Machine Learning for Unforgettable Experiences!
- Machine Learning 101: Understanding the Fundamentals
- Is AI Rigged Against Gamblers? Understanding the Risks
- Machine learning gaming in casinos is inevitable
Is There a Future for AI in Online Casinos?
With recent advancements in artificial intelligence, one question arises – can AI be used in gambling?
Remote gambling has been known for adopting new technologies, with the best online casinos doubling as cutting-edge websites.
Proponents of artificial intelligence would say that most online services that require extensive human interaction with numerous individuals can benefit from “thinking” machines. There are even some proposed implementations of machine learning in gaming.
Better security with AI gambling
Online security is necessary for any service that handles customer funds and data. All UK online gambling sites have SSL encryption and KYC checks for accessing IPs.
However, some new online casinos may want to extend the diligence of their security systems without placing undue pressure on users.
Artificial intelligence provides cybersecurity solutions by dynamically learning malicious practices and automating threat prevention.
This approach meets a sweet spot between enhanced protection for the operator and the user and optimisation.
Artificial intelligence could thus neutralise money laundering concerns, ridding the online casino industry of one of its oldest issues and allegations.
Machine learning in games for cheating detection
We have seen such use of machine learning in gaming industry juggernauts, with Activision’s titles being a notable example.
Cheating verifications in online casinos primarily account for checks of betting patterns that are attributable to automated systems. However, as bots get more competent, their performance can fool rudimentary verifications.
Still, a robust AI-powered cheating detector could dynamically learn new automated patterns and recognise non-human inputs, reducing malicious play, false flags, and potential losses for gambler and operator alike.
Machine learning gambling matchmaking
Similar to the ranking systems for games like Activision Blizzard’s Overwatch pro Leagues, casinos can use AI to provide proper activities and table options for customers.
In our current milieu, most users select their choice of activity based on curated lists for slots sites or live casinos, for example. These come with handpicked examples that human testers have reviewed.
However, this process can, too, be streamlined via AI in gambling. Adjustments can go as far as providing different game variations and betting limits based on the behaviour of gamblers.
Like in most other cases of implementations of ML, gambling curation would only presuppose a better understanding of the customer without it being intrusive.
Better marketing with AI/ML
Marketing is crucial in any online business. In our case, welcome bonuses are often the main attractor for gambling sites.
However, in the industry’s current state, customers usually receive the same type of promotion. Lack of customisation results from a lack of resources on the operator side. In other words, it would take too long for casino operators to create a suited offer for each customer.
Artificial intelligence can come to aid here, too, thanks to its principle of intelligent automation. AI/ML systems can analyse user behaviours and data and develop the best option. More importantly, it will be a personalised option.
AI/ML could help operators provide the same customised experience to all users that only VIP systems showcase nowadays with their dedicated, extensive customer satisfaction models.
We are still far from seeing AI gambling, so the best option for finding promotions is by extensive reviewing and manual checks. This is our exact approach to curating casino bonuses. Think of our reviews as the placeholder for ML systems.
More responsibility with AI gambling
The same approach of including AI in gambling applies to another hot-button issue in the industry: gambling addiction.
The capabilities of ML systems of effectively analysing and dynamically interpreting user data and behaviour can result in a better understanding of customers’ states.
In other words, AI gambling systems could detect addiction in gamers even without it manifesting outright.
Most current methods of staying in control of casino play and stopping gambling addiction entail considerable responsibility on the user’s part. An intelligent recognition system may create an approach to limiting and addressing detrimental behaviours without the user’s input altogether.
How AI Became a Game-Changer for the Gaming Industry

AI and entertainment may not seem the best of partners, but their history indicates the opposite.
One keystone moment for the development and popularity of artificial intelligence was the development of Deep Blue by IBM.
The two-cabinets-wide chess computer was the first machine of its kind to beat a chess champion (Garry Kasparov) at his own game.
Deep Blue vs Kasparov by the BBC
The 1996-1997 game against Kasparov also came with the background of the champion beating Deep Thought, Deep Blue’s predecessor. This event seemed to mark a clear shift in opinion around artificial intelligence and its feasibility.
More recent AI stars in games
In 2011, IBM unveiled Watson, a question-answering computer that went on to compete in a game of “Jeopardy!” against human contestants. Watson won. One may contend that any computer could return a correct answer from a database of questions. However, Watson did more than that.
Watson’s “thinking” process
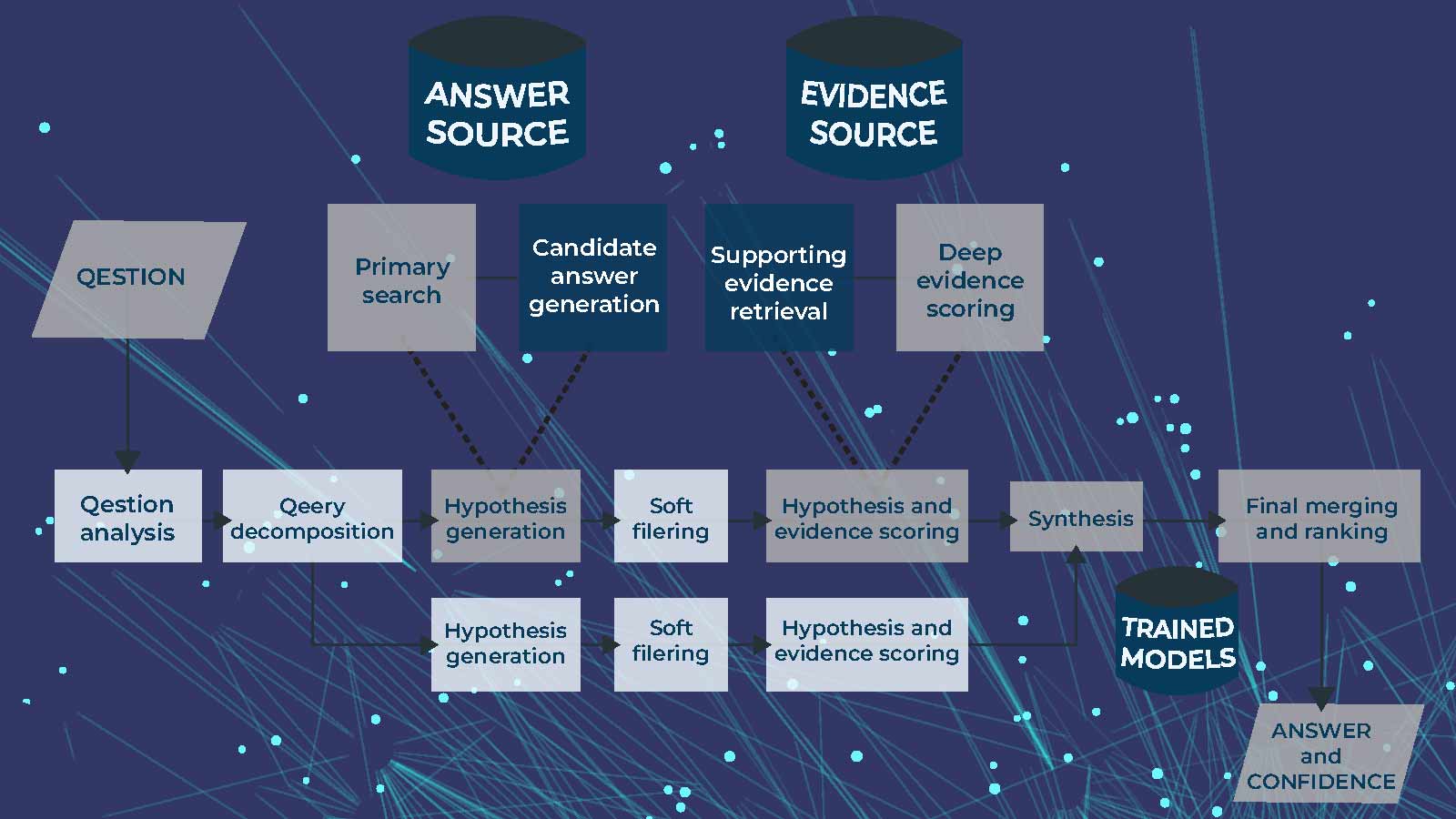
IBM’s Watson was tasked with considering verbal questions and breaking their syntax into the base pieces from which it could search, confirm, and generate an answer.
As the healthcare and life sciences leader at IBM’s Watson New York group, Rob Merkel notes that Watson’s thinking abilities are in four dimensions.
How Watson Processes Questions to Produce Answers
- Linguistic comprehension: It understands language, specifically English, on the same level as human speakers.
- Visual information comprehension: Watson can also understand visual information, such as molecular structures.
- Relation and intent: It can relate information to understand the user’s meaning and provide deeper inquiries to respond to a query.
- Reasoning: When asked questions, humans develop an initial hypothesis and then pursue several others. Watson can consider all such options and return with the best answer.
Nowadays, Watson moved on to more critical jobs, including researching data on cancer prevention-related proteins and reviewing clinical trials to check the effectiveness of drugs.
Using AI and machine learning in games has often been the starting step for multiple projects. Most such thinking machines are then redirected towards more essential tasks.
However, there is potential staying power for machine learning gambling implementations, as proved by already existing uses of AI in gambling.
Taking Gambling to the Next Level with Artificial Intelligence
We have seen some examples of ML and AI in gambling. In some areas, such as sports betting, AI has become a frequent encounter.
The following examples are concrete proof of such systems’ usability and that, with machine learning, gambling can be better, safer, and fairer.
Enhanced responsibility with BetBuddy
Renowned software provider Playtech has acquired responsible gambling analytics platform BetBuddy, intending to create a cutting-edge anti-risk tool. The solution combines ML programming and current research on behavioural patterns in gamblers to provide the first-of-its-kind AI gambling addiction detector. Soon enough, we may see such a system included in all Playtech casino sites, adding one more reason for players to choose their services.
Automated customer service
One of the most widespread uses of AI in gambling is via customer support systems. This is not identical to automated queries that do not adapt to player responses.
You will encounter some online casinos where live chat is handled, at least to some extent, by answer bots. Consider these the younger, less capable counterparts of IBM’s Watson.
As time passes and interactions increase in volume and complexity, these systems will only get better, possibly handling most customer queries, with human interactions being reserved for more complicated and sensitive issues.
AI sports betting
This case of machine learning gambling is not widespread yet, nor is it confirmed, but there is some evidence for it. Exploiting sports betting via machine learning gambling systems has been tried multiple times, with varying success.
Notable AI gambling algorithms
- Purucker’s 1996 Neural Network Model system achieved 61% predicting accuracy for NFL games.
- Khan expanded on Purucker’s work in 2003, achieving 75% accuracy in NFL across 208 matches.
- McCabe and Trevathan arrived at an average 67.5% accuracy with the same model for NFL, AFL, Super Rugby, and EPL in 2010.
- Davoodi and Khanteymooria applied the NN model to horseraces and reached an impressive 77% accuracy following extensive training.
- In 2015, Tax and Joustra achieved an accuracy of 54.7% in Dutch Football competition predictions. The model that used betting odds reached 55.3% accuracy.
Additionally, in an already famous case, the developers of the no-code AI Akkio platform joined forces with expert bettor Chris Rossi to attempt the application of AI in gambling. However, they would judge the results based on placed wagers and returns this time.
The first attempt (where Rossi did not place wagers) would have yielded a return on investment of 140%.
When Rossi actually placed bets based on Akkio’s guesses, he succeeded in seven out of 16 races, making around $136 for the wagered $70. The 43.75% accuracy rate does not raise any eyebrows, but it is ten points higher than the success rate of the betting public.
More importantly, Akkio closely mirrored the post-time odds, leading to a startling realisation.
Bookies may already employ sports betting AI
There are two indicators that operators may use AI sports betting predictors.
- Akkio’s close matching of post-time odds suggests that bookmakers generate them similarly.
- Tax and Joustra’s 2015 Neural Network model reached a higher accuracy based on the betting odds.
Kaunitz, Zhong, and Kreiner provided the most complex and broadly tested investigation of ML based on odds. Their paper ends with two damming conclusions for sports betting, the first being that bookies are likely to use ML systems themselves to generate odds. Lastly, just like arbitrage betting, being too good with your predictions (thanks to machine learning gambling models) may attract discriminatory actions from bookmakers.
Can AI help casinos cut down on problem gambling?

This discussion rages on, with proponents and opponents battling on multiple fronts, including the feasibility, intention, and overall incentive of responsible AI gambling.
What is clear is that the casino industry already has solutions that go beyond Playtech’s BetBuddy.
Midway AI is a Danish company that grew out of Aarhus University. Using the aid of psychologists, its developers manifest to train it to recognise and identify problem gambling behaviours.
Case closed, some may say. However, just as Midway’s chief executive, Mr Kjærgaard contends, there are several difficulties to having effective identification. While most operators use the time and money spent by customers as sole indicators, Midway AI accounts for 14 different factors.
Midway’s fields of analysis include
- Time and money spent.
- Cancelled withdrawals
- Shifts in the periods of play across the day
- Erratic play patterns.
Midway’s program would flag at-risk gamblers based on psychologically backed areas of verification. However, this is where issues arise.
Players are reluctant to reduce their gameplay when experiencing an issue. They will be even more resistant to a notification informing them that an AI algorithm identified them as potentially at-risk.
AI gambling checks, beyond online casinos
Another example of AI in gambling comes from Macau.
The Asian gambling capital has constantly been on the cutting edge of the industry, notwithstanding the Macau gambling losses it recently experienced.
Macau’s operators have several monitoring systems, including hidden cameras with facial recognition technologies and chips containing radio-frequency identification systems. They use these to collect data on customer behaviour and detect instances of collusion between players.
While not directly related to safer gambling, similar systems could be employed to create dynamic profiles for all customers and identify behavioural risks in time.
Is there an interest in machine learning gambling solutions?
Most implementations of AI in gambling came from third parties, this being the case for BetBuddy and Midway AI.
Lia Nower, the director of the Centre for Gambling Studies at Rutgers, aptly indicated that most operators might be uninterested in investing in fancy ML systems for detecting player addiction as they lack any profit motive.
Gambling companies have been more open to AI in gambling marketing and ads, with safe play taking a backseat.
The desire and higher adoption rates of machine learning gambling algorithms will most certainly depend on updating regulations and strictures, as well as customer demand.
For now, regulators and AI gambling solutions developers should bring home the message that machine learning responsible gambling tools provide extended protections without being as intrusive or blunt as previous measures.
Next-Gen Gambling Awakens: Harnessing the Power of Machine Learning for Unforgettable Experiences!

There is a long history of AI and machine learning in gaming industry sectors.
AlphaGo
We have previously discussed the use of Deep Blue in chess. Still, there were similar implementations in Go (which is considered to pose more difficult AI problems, having 10170board states compared to 10120states in chess), with Google’s AlphaGo being the first such agent to beat a pro (human) player. This model also has a better implementation, AlphaGo Zero, which can play with itself and improve its skills.
Alphastar
DeepMind’s Alphastar was the first to beat professional StarCraft II players without any advantages. More interestingly, following optimisations, it could win by using the camera just like human players.
OpenAI
OpenAI designed an ML program that managed to beat the 2018 Dota 2 champions.
Planetary Annihilation and ANNs
Planetary Annihilation used artificial neural networks in the default AI agent’s design.
Vision-based models
Programs that learn to understand visual input and learn based on digital images or videos were created for Pong, Atari titles, Doom, Super Mario, and Minecraft.
Neuroevolution in games
Galactic Arms Race uses neuroevolution (AIl that uses evolutionary algorithms to generate ANNs, topology, parameters, and rules) to create unique weapons for the player.
PCG creation
Super Mario Bros. and The Legend of Zelda have been used to stimulate PCG level creation.
The future of machine learning gaming industry sectors
ANNs may play a further role in creating better AI and NPC behaviours in video games.
Similar to the Galactic Arms Race’s use of it, neuroevolution could be used for procedural generation of all types, from mapmaking to emergent rulemaking.
Lastly, the capability shown by AI models to beat professional humans may signal that there will be a time when the best esports games will be dominated by self-teaching tech and machine learning programs.
Operators can also combat cheating in ranked game matches similar to the systems constructed for gambling.
Machine Learning 101: Understanding the Fundamentals
Machine learning or ML is a field of study centred around creating methods of “learning”, i.e., using existing data to improve performance in a task.
The field already has several applications, from speech recognition, email filtering, computer vision, and even picture generation. The latter recently grabbed the limelight with domains like DALL·E 2.
How is machine learning different?
Traditionally, the programming paradigm implied a programmer creating a program that, based on input to be understood as observations, generates an output.
Machine learning aims to take inputs and outputs and generate a program from them.
Three broad types of ML
- Supervised learning: takes labelled data, has direct feedback, and predicts an outcome.
- Unsupervised learning: has no labels, no feedback, and finds the hidden structure of the data.
- Reinforcement learning: has a decision process and reward system and learns a series of actions.
How is it different from AI?
Machine learning grew out of early approaches to artificial intelligence. Where they historically differ is precisely how the developed models learn and adapt.
ML systems assimilate data passively, with their approach being statistical and probabilistic. Comparatively, artificial intelligence entails symbolic processing and interaction with the environment.
Consequently, ML is much more tied to concepts such as probabilistic thinking, statistical inference, and fuzzy logic, while AI has a more logical, epistemological approach.
Some will say that ML is a subset of AI. A better overview is that AI and ML partially overlap, their common ground closely tied to deep learning.
Artificial general intelligence and narrow AI
Artificial intelligence can be further divided into narrow AI, i.e., active, logical learning systems that specialise in one task, and AGI.
The latter aims to be a multipurpose system that can mimic human intelligence across as broad a range of tasks as possible.
Is AI Rigged Against Gamblers? Understanding the Risks

No matter if we get to see extensive use of AI in gambling, its implementation may skew the odds in one side’s favour.
The possible introduction of the new technology thus begs the question: who is most helped by machine learning gambling?
The house’s sports betting AI would indicate
ML requires a broad set of data, computation time, and power to perform well. Similarly, AI systems require processing power and extensive learning periods to work.
While independent gamblers may implement their machine learning gambling systems to gain an edge, you now know that bookies and operators may already do that for formulating odds.
In this case, companies can use their extensive database to generate more educated AI/ML systems that maintain their edge.
Machine learning gambling ads are here
One way in which we have already seen ML and AI in gambling is through marketing.
Most operators will employ data processing systems, often powered by artificial neural networks, to create the most appealing ads for their products.
This may entice the average gambler, as it learns one’s preferences and creates dedicated offers. However, it will help the operator attract and maintain a customer base.
AI gambling helps the gambler, but not with winning
Responsible gambling systems may benefit from AI/ML applications. We have already seen examples with BetBuddy and Midway AI.
However, these options and still a niche and have yet to become widely used and appealing solutions in the industry.
Nonetheless, there is perhaps no better example of machine learning and AI in gambling that will help you as a customer.
Machine learning gaming in casinos is inevitable
Most online industries have adopted AI/ML systems to some extent. Marketing benefits from it, as does cybersecurity.
If you are wondering why data collection (often via “free” services, such as social media platforms) has become so crucial because AI/ML solutions use it to tweak several types of processes for the companies in question.
For better or worse, AI and ML are here to stay, and online gambling is no exception. However, how this adoption will manifest depends on the diligence of regulators, vigilance of its customers, and operators’ performance.
AI in gambling could mark a new revolution in the industry, but only if it is introduced to support all implicated sides.















